Core Concepts
1. Service Packages Configuration#
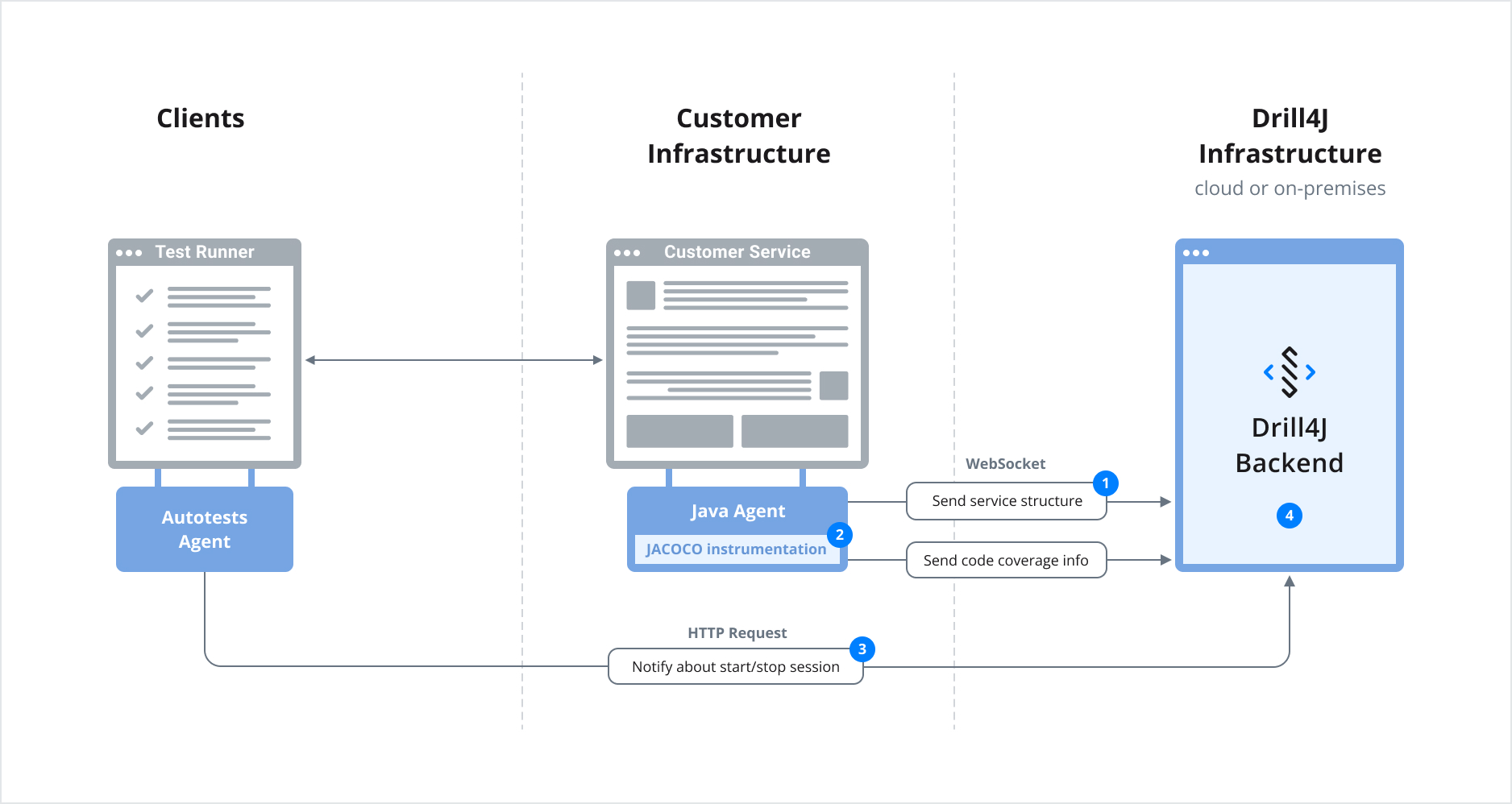
The Drill4J Agent sends the application structure (packages\classes\methods) to the Drill admin panel.
User is able to configure which service (application) packages will be instrumented. It can be done on the 2nd step of agent registration in the field Application Packages.
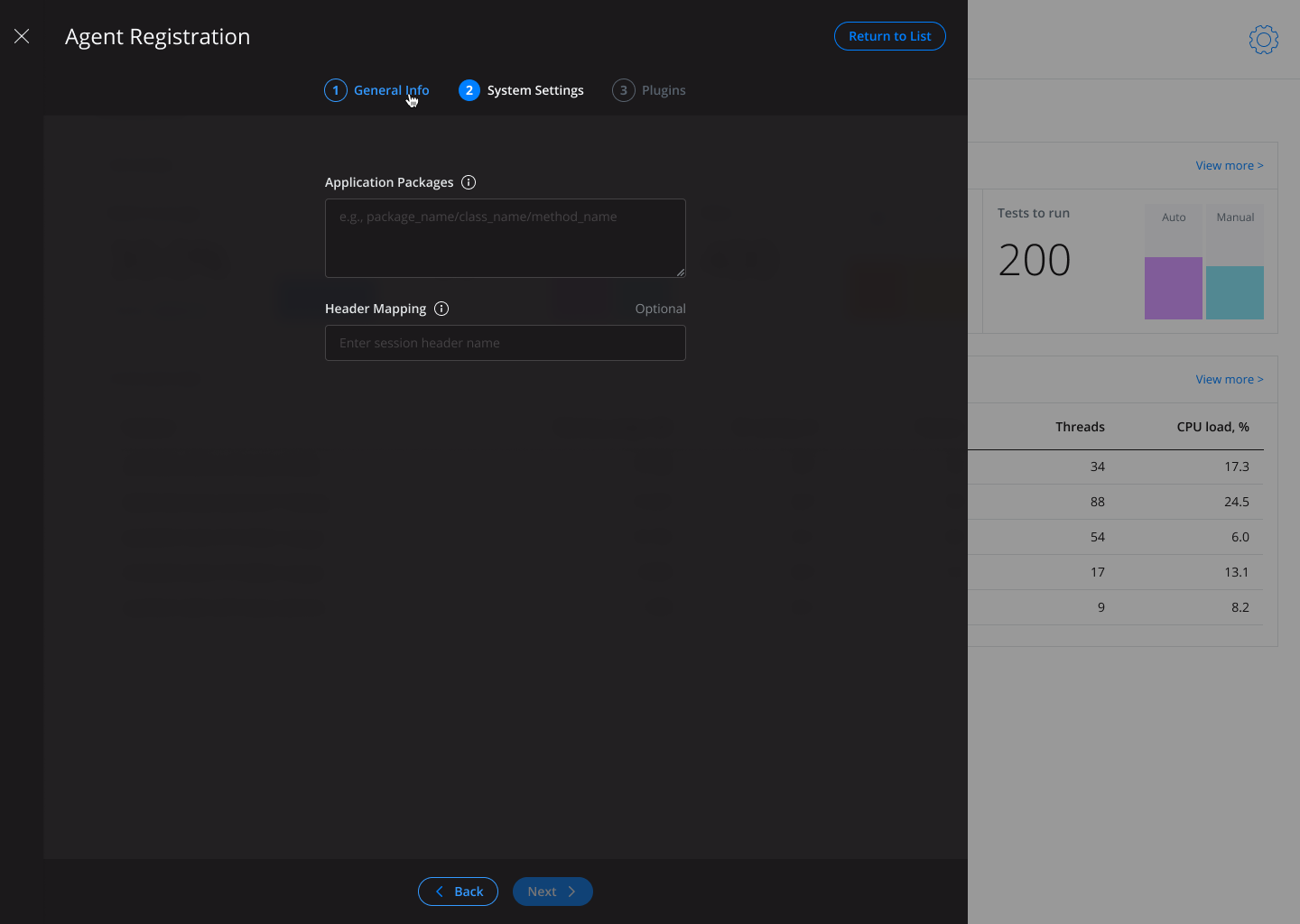
A line with hyphenation turns into an array of strings for backend.
2. Runtime Code Instrumentation with JaCoCo#
Code is instrumented with JaCoCo. Instrumentation allows the Drill4J agent to track code execution during tests. All instrumentation is happening in runtime. There is no need to change either original sources nor build files.
JaCoCo Overview#
JaCoCo is a free code coverage library for Java, that calculates coverage by probes.
Probes - boolean array.
For example:
[f,f,f,f,f,f,f.......], where f - false means that in the process, our thread of execution did not come across a line of code. This probes list exists for each class.
Probes are placed in different places (e.g.):
- at the beginning of the method
- at the beginning of the branch block
Code Coverage Calculation Algorithm#
First, probes are put down with the help of instrumentation in the source code.
When the code is executed, the probe becomes TRUE in the boolean array.
Analysis of all probes and coverage calculation is described in documentation.
Bytecode instrumentation is described in documentation.
3. Context Propagation#
Autotest Agent tracks code execution for each test separately and reports these data to Drill4J Admin Backend. It integrates with various testing frameworks and configures Selenium to add headers to the HTTP requests. It's necessary to connect a particular test of a User with a Drill4J agent, we need to add additional information in the form of a User identifier (session id) and a test identifier within HTTP requests. We implement an interceptor for each (supported) client (e.g. Apache, okhttp, Netty) using instrumentation.
4. Metrics Calculation#
Drill4J Admin Backend calculates the following metrics:
- test coverage
- associated tests
- covered methods
- risked methods
- recommended tests
- quality gate status
Risked Methods#
Risked methods are New or/and Modified methods detected in a new application build. Risk is considered covered if it was covered on any percent.
E.g. in the current build 1000 New methods (200 uncovered), 500 modified (101 uncovered), than risked methods number = 200 + 101 = 301 risked methods.
Lambdas aren't displayed as the risked method and not taken in build difference calculation.
A risked method has 3 states:
- not covered
- partially covered
- fully covered
Recommended Tests#
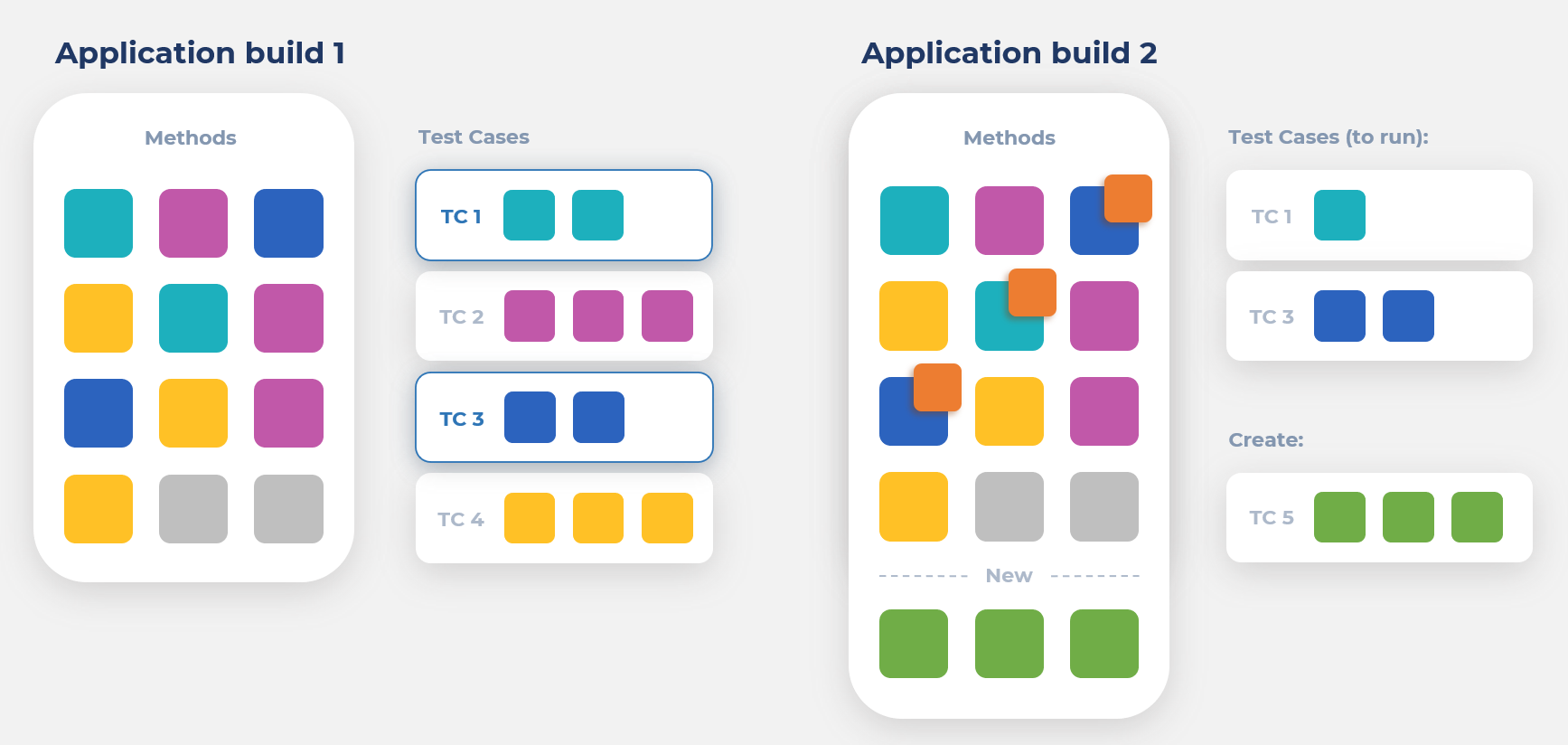
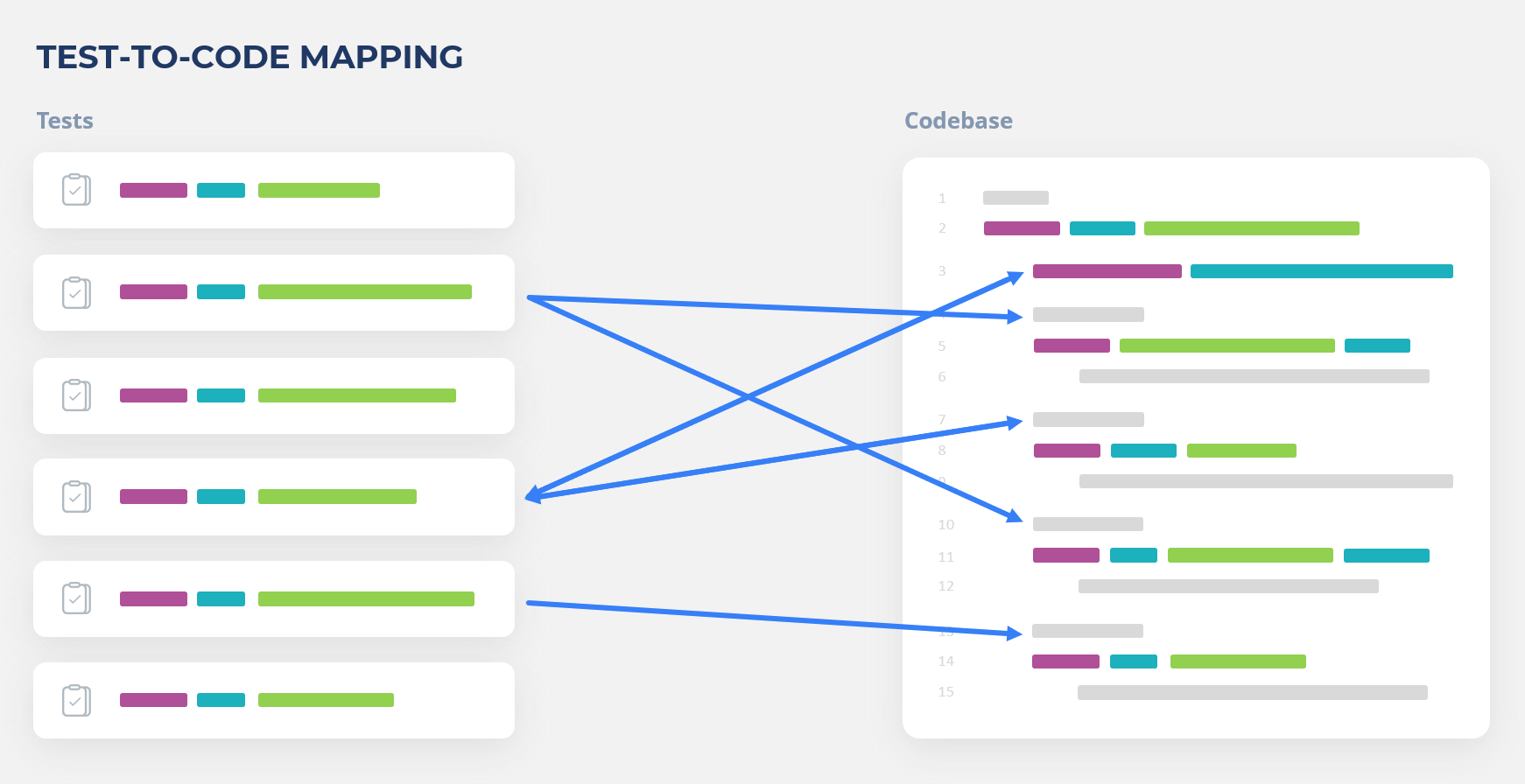
Recommended tests are tests that should be run at first to check changes of code in a new application build. The set of recommended tests is formed by Test to Code mapping. It's a relationship between a particular test with the executed part of code.
E.g. In the first application build tests are mapped to code. The second application build has 3 modified methods which were covered by 2 test cases (autotests).
Related to this information, we recommend to run only 2 test cases in order to check only modified code and don't waste time to run cases that aren't check something useful.
Also, we recommend writing new autotests or modify existing autotests to cover new methods.